1. Molecular Framework and Physical Feature
1.1 Chemical Composition and Polymer Architecture
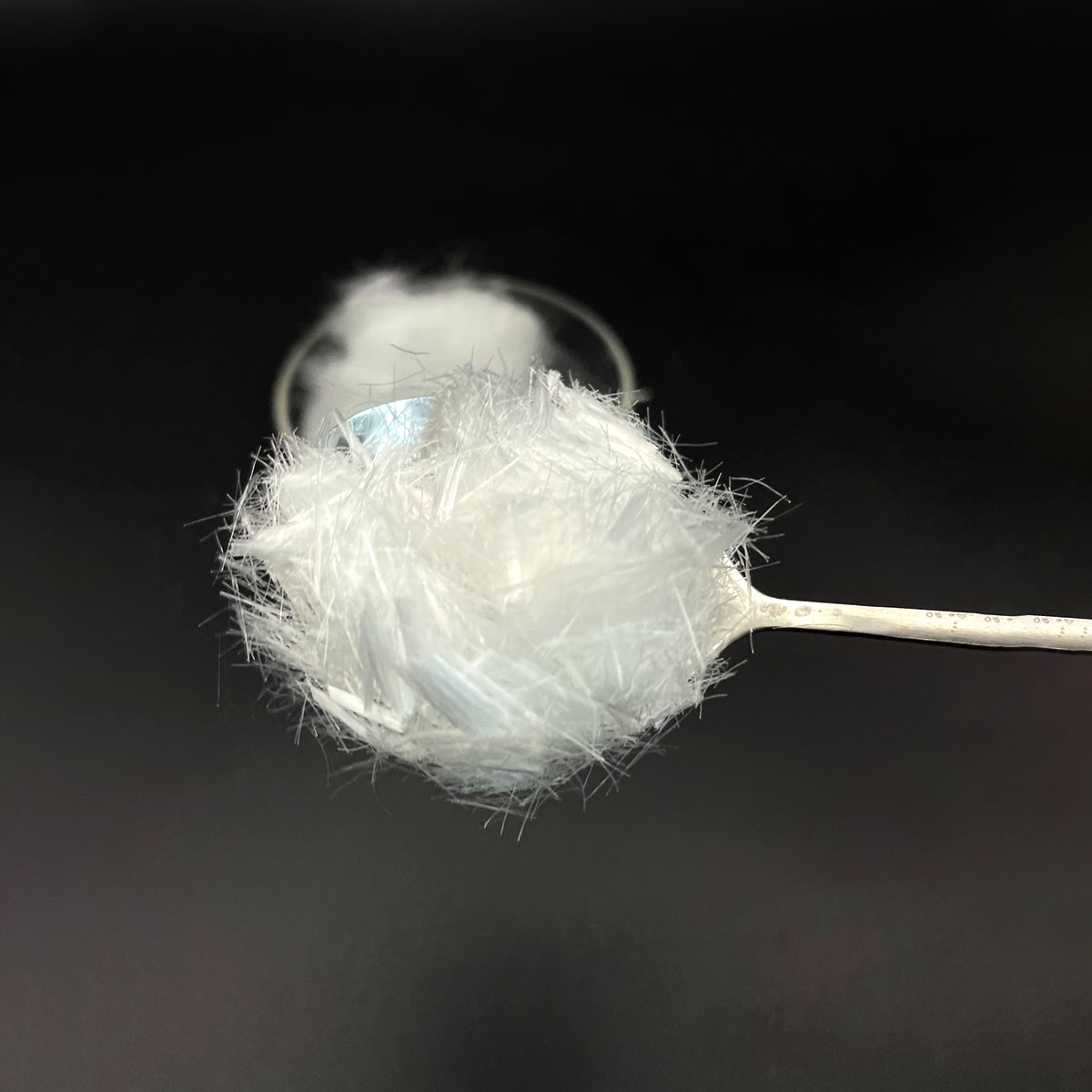
(PVA Fiber)
Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber is a synthetic polymer originated from the hydrolysis of polyvinyl acetate, leading to a direct chain composed of duplicating–;(CH ₂–; CHOH)–; units with differing levels of hydroxylation.
Unlike most synthetic fibers created by direct polymerization, PVA is normally manufactured via alcoholysis, where plastic acetate monomers are initial polymerized and after that hydrolyzed under acidic or alkaline problems to replace acetate teams with hydroxyl (–; OH) capabilities.
The level of hydrolysis–; varying from 87% to over 99%–; seriously influences solubility, crystallinity, and intermolecular hydrogen bonding, thus dictating the fiber’;s mechanical and thermal habits.
Completely hydrolyzed PVA displays high crystallinity because of extensive hydrogen bonding between nearby chains, resulting in premium tensile toughness and minimized water solubility compared to partially hydrolyzed kinds.
This tunable molecular style permits accurate design of PVA fibers to meet details application requirements, from water-soluble momentary assistances to long lasting architectural supports.
1.2 Mechanical and Thermal Features
PVA fibers are renowned for their high tensile strength, which can surpass 1000 MPa in industrial-grade variants, matching that of some aramid fibers while maintaining better processability.
Their modulus of elasticity varieties between 3 and 10 Grade point average, giving a beneficial balance of rigidity and adaptability appropriate for textile and composite applications.
A key distinguishing feature is their extraordinary hydrophilicity; PVA fibers can take in as much as 30–; 40% of their weight in water without dissolving, depending upon the degree of hydrolysis and crystallinity.
This residential or commercial property makes it possible for rapid dampness wicking and breathability, making them optimal for medical textiles and hygiene products.
Thermally, PVA fibers display great stability as much as 200 ° C in dry conditions, although extended exposure to warmth generates dehydration and discoloration due to chain deterioration.
They do not thaw however decay at elevated temperature levels, releasing water and developing conjugated frameworks, which restricts their use in high-heat atmospheres unless chemically changed.
( PVA Fiber)
2. Manufacturing Processes and Industrial Scalability
2.1 Wet Spinning and Post-Treatment Techniques
The main technique for creating PVA fibers is damp rotating, where a concentrated aqueous service of PVA is extruded with spinnerets into a coagulating bathroom–; generally including alcohol, not natural salts, or acid–; to speed up solid filaments.
The coagulation procedure controls fiber morphology, diameter, and positioning, with draw ratios throughout rotating affecting molecular placement and supreme strength.
After coagulation, fibers undertake numerous drawing stages in hot water or heavy steam to boost crystallinity and positioning, substantially improving tensile residential or commercial properties via strain-induced crystallization.
Post-spinning treatments such as acetalization, borate complexation, or warmth treatment under tension further modify efficiency.
As an example, therapy with formaldehyde produces polyvinyl acetal fibers (e.g., vinylon), boosting water resistance while maintaining stamina.
Borate crosslinking creates relatively easy to fix networks helpful in clever fabrics and self-healing products.
2.2 Fiber Morphology and Functional Modifications
PVA fibers can be engineered into different physical types, including monofilaments, multifilament threads, short staple fibers, and nanofibers produced by means of electrospinning.
Nanofibrous PVA mats, with diameters in the range of 50–; 500 nm, offer incredibly high surface area-to-volume ratios, making them superb candidates for purification, drug delivery, and cells design scaffolds.
Surface alteration techniques such as plasma therapy, graft copolymerization, or finish with nanoparticles enable customized capabilities like antimicrobial activity, UV resistance, or enhanced attachment in composite matrices.
These adjustments expand the applicability of PVA fibers beyond conventional usages right into sophisticated biomedical and ecological modern technologies.
3. Useful Characteristics and Multifunctional Behavior
3.1 Biocompatibility and Biodegradability
One of one of the most significant advantages of PVA fibers is their biocompatibility, permitting risk-free usage in direct contact with human tissues and liquids.
They are widely employed in surgical stitches, injury dressings, and man-made body organs due to their non-toxic degradation items and marginal inflammatory response.
Although PVA is naturally immune to microbial strike, it can be provided biodegradable with copolymerization with biodegradable systems or enzymatic treatment making use of bacteria such as Pseudomonas and Bacillus species that produce PVA-degrading enzymes.
This dual nature–; persistent under typical problems yet degradable under regulated biological atmospheres–; makes PVA suitable for temporary biomedical implants and green product packaging remedies.
3.2 Solubility and Stimuli-Responsive Actions
The water solubility of PVA fibers is an unique practical feature made use of in varied applications, from momentary textile supports to controlled launch systems.
By readjusting the degree of hydrolysis and crystallinity, suppliers can customize dissolution temperature levels from room temperature to above 90 ° C, making it possible for stimuli-responsive behavior in clever materials.
For instance, water-soluble PVA threads are used in needlework and weaving as sacrificial supports that dissolve after processing, leaving elaborate textile frameworks.
In agriculture, PVA-coated seeds or fertilizer pills release nutrients upon hydration, boosting effectiveness and lowering drainage.
In 3D printing, PVA acts as a soluble assistance product for complex geometries, liquifying easily in water without harming the primary framework.
4. Applications Across Industries and Emerging Frontiers
4.1 Fabric, Medical, and Environmental Uses
PVA fibers are thoroughly utilized in the textile industry for producing high-strength fishing webs, industrial ropes, and blended fabrics that improve longevity and dampness management.
In medicine, they develop hydrogel dressings that preserve a damp wound environment, advertise recovery, and reduce scarring.
Their capacity to create transparent, flexible movies additionally makes them ideal for get in touch with lenses, drug-eluting spots, and bioresorbable stents.
Ecologically, PVA-based fibers are being established as alternatives to microplastics in detergents and cosmetics, where they liquify completely and prevent long-term pollution.
Advanced filtering membrane layers incorporating electrospun PVA nanofibers successfully record fine particulates, oil droplets, and even infections due to their high porosity and surface capability.
4.2 Support and Smart Product Assimilation
In building and construction, brief PVA fibers are contributed to cementitious composites to improve tensile toughness, split resistance, and effect sturdiness in engineered cementitious composites (ECCs) or strain-hardening cement-based products.
These fiber-reinforced concretes show pseudo-ductile behavior, with the ability of withstanding substantial contortion without tragic failing–; ideal for seismic-resistant structures.
In electronics and soft robotics, PVA hydrogels work as adaptable substrates for sensing units and actuators, replying to humidity, pH, or electric fields through relatively easy to fix swelling and reducing.
When integrated with conductive fillers such as graphene or carbon nanotubes, PVA-based composites work as elastic conductors for wearable tools.
As study developments in sustainable polymers and multifunctional products, PVA fibers remain to become a versatile system bridging performance, security, and environmental obligation.
In recap, polyvinyl alcohol fibers stand for an unique course of synthetic products combining high mechanical efficiency with extraordinary hydrophilicity, biocompatibility, and tunable solubility.
Their adaptability across biomedical, commercial, and environmental domains emphasizes their essential role in next-generation material science and sustainable modern technology growth.
5. Distributor
Cabr-Concrete is a supplier under TRUNNANO of Calcium Aluminate Cement with over 12 years of experience in nano-building energy conservation and nanotechnology development. It accepts payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union and Paypal. TRUNNANO will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by air, or by sea. If you are looking for pva fiber reinforced concrete, please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry.
Tags: pva fiber,polyvinyl alcohol fiber, pva concrete
Omnia vasa et picturae e Internet sunt. Si quae sunt Copyright quaestiones, Quaeso contact us in tempore delere.
Inquirere nos